
DADiSP Online Help
Click here to see this page in full context

DADiSP Worksheet Functions > Function Categories > Fourier Transforms and Signal Processing > ZHPFILT
Performs high pass filtering by zeroing the FFT values.
ZHPFILT(series, fc, mask)
|
series |
- |
Input series to filter. |
|
fc |
- |
Optional. A real, the high pass cutoff frequency. Defaults to |
|
mask |
- |
Optional. An integer, return the frequency domain mask only. Defaults to 0, return processed input. |
A series, the high pass filtered output.
W1: gsin(1000, 1/1000, 20) + gsin(1000, 1/1000, 1)
W2: zhpfilt(w1, 10)
W1 contains a 20 Hertz sinewave riding on top of a 1 Hertz sinusoidal drift.
W2 filters out the drift an returns the 20 Hertz sinusoidal component.
ZHPFILT performs high pass filtering by zeroing out the low frequency components of the FFT of the input. FFT zeroing is a crude but fast filtering operation. However, the pass band and transition edge of the equivalent filter will exhibit significant ripple.
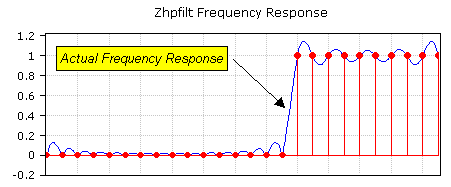
For a flatter response, use traditional filter design methods such as those offered by DADiSP/Filters.
If fc < 0, no filtering is performed.
If mask == 1, the frequency domain binary mask used to zero out the stop band frequencies is returned.
See ZLPFILT for a low pass filter.