
DADiSP Online Help
Click here to see this page in full context

Calculates the two-dimensional (2D) FFT of an array.
FFT2(a, rowlen, collen)
|
a |
- |
An array. |
|
rowlen |
- |
Optional. An integer. The FFT row size. Defaults to |
|
collen |
- |
Optional. An integer. The FFT column size. Defaults to |
A complex array.
fft2({{1, 2}, {3, 4}})
returns the complex array:
{{10+0i, -2+0i},
{-4+0i, 0+0i}}
(x, y) = fxyvals(-2, 2, .1, -2, 2, .1);
W1: cos(x*y);setplottype(3);rainbow
W2: fft2(W1)
W3: fftshift(log10(mag(W2)))
W4: fftshift(phase(W2))
Produces interesting 2D magnitude and phase images.
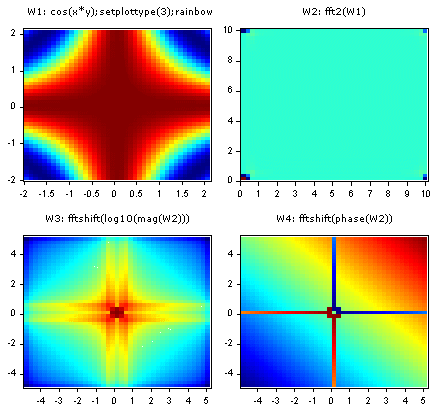
FFT2 is often used in image processing applications. Use FFTSHIFT to flip the output so the 0 frequency is in the center of the plot.
If rowlen is larger than the number of input rows or collen is greater than the number input of columns, the input is zero-padded.
If the input data is a series (i.e. a single column), a 1D FFT is performed.